5-year-old male crossbreed hit by a car with tetraplegia and cervical pain. A cervico-thoracic spine CT was performed.

Description
There are multiple fractures of the C6, C7, T1, T2 and T3 vertebrae.
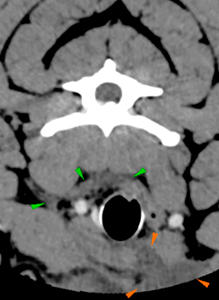
There is a complete mild displaced fracture of the right transverse process (green arrows) of C6, and a complete caudodorsal displaced fracture of the right transverse process of C7 (pink arrows).
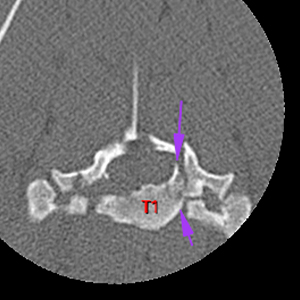
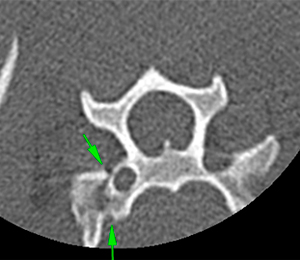
There are multiples fractures of T1: complete minimally displaced fractures of both cranial articular process (yellow arrows), fracture of the left craniodorsal aspect of the vertebral body (purple arrows). There is a comminute dorsally displaced fracture of the right dorsal lamina and pedicle with completely separation of the right transverse process and right costal fovea with dorsal displacement of the right costal head (red arrows). These fractures cause a complete separation of the spinous process of T1.
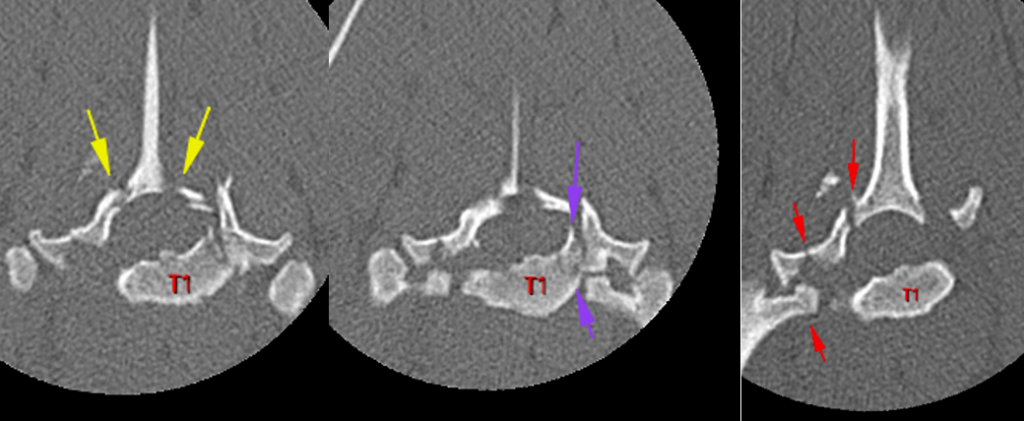
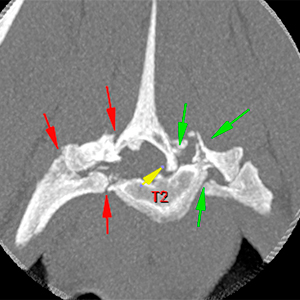
There are fractures of the left cranial articular process and a comminute fracture of the left lamina and pedicle of T2 with complete separation of the left transverse process and left costal fovea (green arrows).
The right lamina and pedicle have a comminute fracture with complete separation of the right transverse process and costal fovea (red arrows). These fractures cause a complete separation of the spinous process of T2 that is ventrally displaced within the vertebral canal (yellow arrow) and there is loss visualization of the epidural fat.
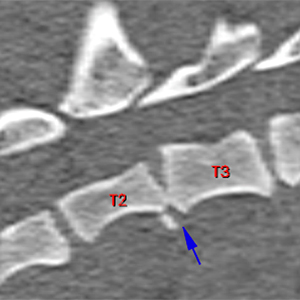
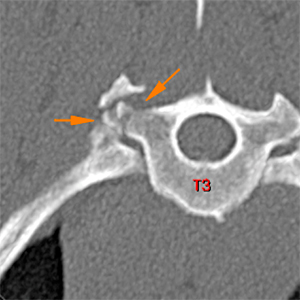
There is a fracture of the right caudal aspect of the caudal endplate of T2, causing a marked narrowing of the T2-T3 intervertebral space (blue arrow). There is a comminute fracture of the right transverse process of T3 without affection of the head of the rib (orange arrows).
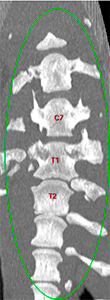
There is a left shift of the longitudinal vertebral axis at the level of T1-T2 (green oval).
Large amount of free air is observed in the left dorsal pleural space (pink arrows) and mild amount of this is seen in the right pleural space (green arrows). The left lung parenchyma is ventrally retracted with areas of increased attenuation.
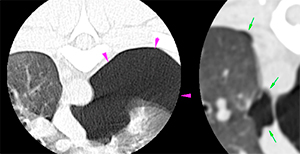
The cervical musculature is partially included in the spinal CT. The left sternocephalic and sternohyoid muscles are moderately thickened with hypoattenuating central areas (orange arrows). The subcutaneous and adipose tissue of the ventral neck is thickened and increased attenuation (green arrows).
Diagnosis
- Vertebral instability at the level of T1-T3 due to multiples vertebral fractures.
- Ventral displacement of the spinous process of T2 occupying the vertebral canal and left shift of the longitudinal cranial thoracic vertebral axis.
These findings are most likely consistent with medullary compression at the level of T2, which is not clearly visible on the CT.
- Fractures of the transverse processes of C6, C7 and T3.
- Bilateral pneumothorax (left > right) and multiple pulmonary areas of increased attenuation, most likely secondary to trauma – haemorrhage, pulmonary contusion – or related to atelectasis due to pneumothorax.
- Multifocal myopathy of the ventral musculature of the neck and oedema of the ventral subcutaneous tissue, most likely secondary to trauma.

No comment yet, add your voice below!