9 -years-old female domestic short hair. A tubular adenocarcinoma was diagnosed by biopsy in the dorsal aspect of the thoracic region. A thoracic CT was performed. A thoracolumbar spine and thoracic CT scan was performed.

Description
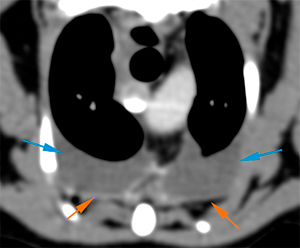
There is a moderate homogeneous bilateral pleural effusion in the ventral aspect of both hemithorax (blue arrows). The post-contrast series show a mild diffuse thickening of the parietal pleura (orange arrows).
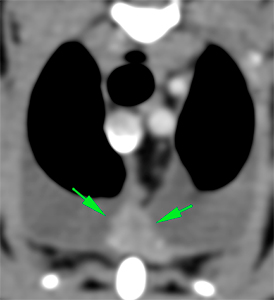
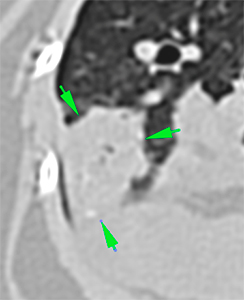
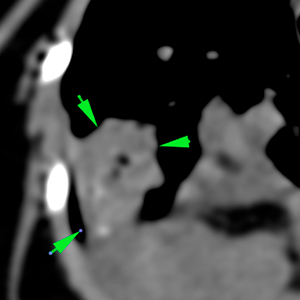
The sternal lymph nodes are moderately enlarged with homogeneous post-contrast enhancement (green arrows -). The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are markedly enlarged and show a heterogeneous rim contrast enhancement (orange arrows). Both main bronchi are mildly displaced and compressed because of the enlarged tracheobronchial lymph nodes (blue arrows).
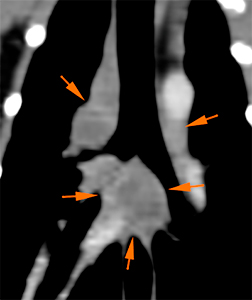
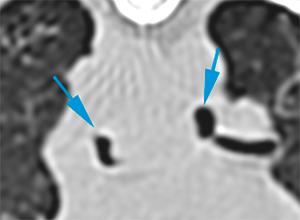
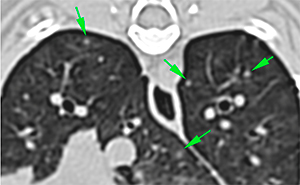
There are multiple, variable in size, diffuse soft tissue nodules in the lung parenchyma, some of them with irregular margins and a moderate contrast enhancement (green arrows). In addition, there are other ill-defined nodular lesions in multiple lung lobes.
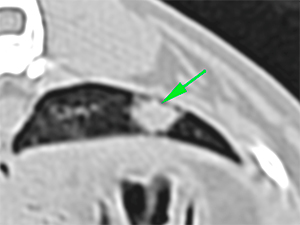
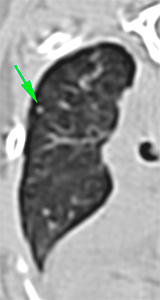
In the ventral aspect of the right middle lung lobe, there is a hyperattenuating area with irregular margins and heterogeneous contrast enhancement that shows multiple mineral foci within it (green arrows).
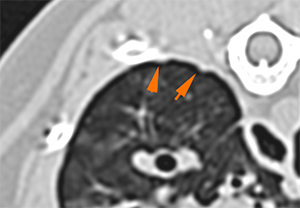
There are multiple small nodular and plaque-like areas of subpleural thickening (orange arrows).
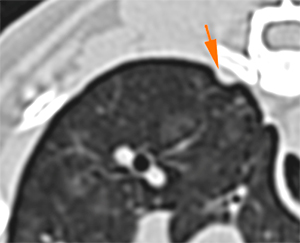
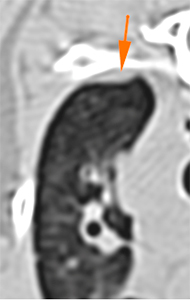
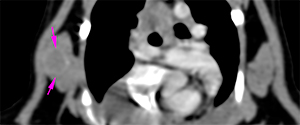
In the 5th/6th intercostal space, at the level of the right ventral serratus muscle, there is an ill-defined, rim enhancing, nodular lesion (pink arrows).
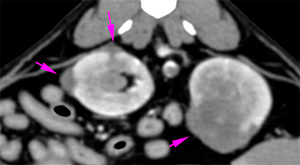
In the abdominal structures included in the CT, there are multiple irregular soft tissue lesions in both kidneys that show heterogeneous contrast enhancement. These lesions disrupt the normal renal architecture and protrude the renal cortex (pink arrows). The largest lesion is located at the medial aspect of the left kidney.
Diagnosis
- Multiple pulmonary nodules, most likely consistent with pulmonary metastasis given the clinical history.
- Lesion at the right middle lung lobe: most likely consistent with metastasis. A primary pulmonary lesion, such as pulmonary carcinoma, cannot be ruled out.
- Subpleural nodules and diffuse pleural thickening, most likely consistent with neoplastic infiltration – carcinomatosis -.
- Sternal and tracheobronchial lymphadenopathy most likely consistent with metastasis.
- Moderate bilateral pleural effusion
- Nodule in the right costal musculature most likely consistent with metastasis.
- Nodular renal lesions: most likely consistent with metastasis; primary renal neoplasia cannot be ruled out but it is considered less likely.
Comments
The lesions observed in the lung, kidney, pleura, lymph nodes and musculature are most likely consistent with a neoplastic process (carcinoma, most likely, based on the characteristics and biopsy of the excised lesion; other types of neoplasia, such as sarcoma or lymphoma, are less likely). Other differentials diagnosis are unlikely. Due to the multifocal pattern, it is difficult to determine which of the lesions is the primary lesion, and which ones are metastases.
Fine needle aspiration of some of the renal lesions (left kidney), pulmonary lesions, lesion in the costal musculature and analysis of the pleural effusion are recommended in order to reach a definitive diagnosis.

No comment yet, add your voice below!