7-year-old male Boxer with ataxia, disorientation and loss of balance that does not respond to treatment. A head Ct scan was performed.

Description
There is a pedunculated lesion with cystic appearance in the nasopharynx, extending through a bone defect into the pituitary fossa. The lesion is well defined, fluid attenuating and is not associated with any aggressive osseous changes or significant compression of the brain parenchyma, although it occupies the pituitary fossa (yellow arrows).
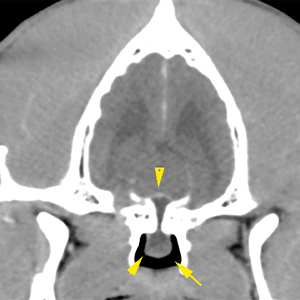
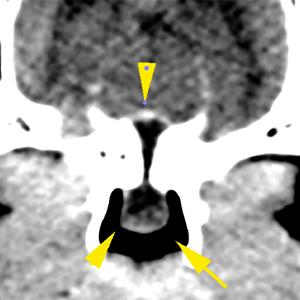
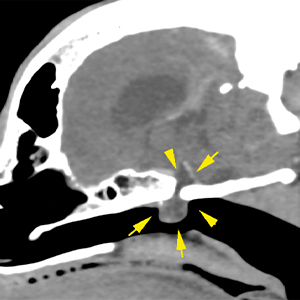
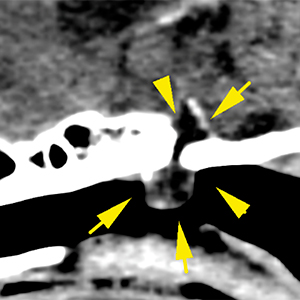
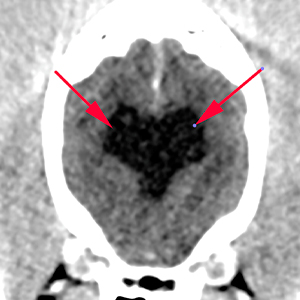
The lateral ventricles are moderately distended and symmetric (red arrows). They are communicated with absence of septum pellucidum. There are no other intracranial abnormalities without evident extra- or intra-axial lesions.
Diagnosis
- Lesion with cystic appearance and benign characteristics, extending from the pituitary fossa towards the nasopharynx. The lesion is consistent with a Rathke’s cleft cyst. Other differentials are unlikely.
- Ventriculomegaly of the lateral ventricles most likely incidental and breed related.
Comments
Rathke’s cleft cysts are uncommon lesions of congenital origin that may not be associated with any clinical signs, although they are also described as causing nasopharyngeal obstructions or dwarfism. In this case, the relation between the lesion and the clinical signs is uncertain and the symptoms could be due to idiopathic vestibular syndrome. However, subtle vascular or inflammatory/infectious lesions cannot be completely ruled out, given that the CT is not sensitive to subtle changes. To rule out these pathologies, CSF analysis or MRI are recommended, if clinically indicated.
The following might be of interest:
- Hasegawa, D., Uchida, K., Kobayashi, M., Kuwabara, T., Ide, T., Ogawa, F., … & Orima, H. (2009). Imaging diagnosis—Rathke’s cleft cyst. Veterinary Radiology & Ultrasound, 50(3), 298-300.
- Beck, J. A., Hunt, G. B., Goldsmid, S. E., & Swinney, G. R. (1999). Nasopharyngeal obstruction due to cystic Rathke’s clefts in two dogs. Australian veterinary journal, 77(2), 94-96.

No comment yet, add your voice below!