7-year-old female neutered French Bulldog. Left middle ear disease is suspected. A head CT scan was performed.

Description
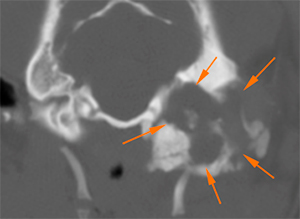
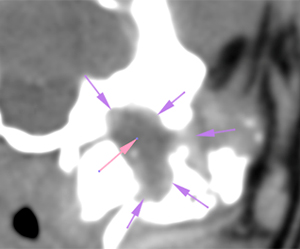
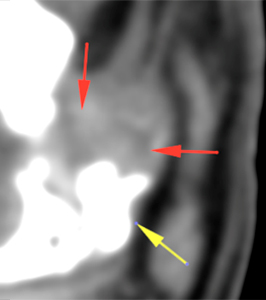
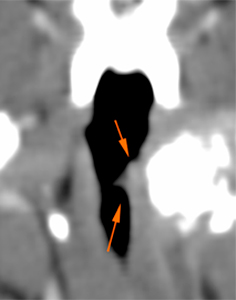
At the left tympanic bulla, there is an expansile osseous lesion (orange arrows), which causes distortion of the tympanic bulla. Its wall shows markedly irregular areas of thickening (blue arrows), and other areas of discontinuity with lysis of the wall (green arrows). The tympanic bulla is completely obliterated by a soft tissue attenuating material (pink arrow), showing a marked peripheral post-contrast enhancement (violet arrows). The horizontal portion of the external ear canal is completely obliterated, occupied by a material of similar characteristics (red arrows) and with marked thickening and mineralization of its wall (yellow arrows). The vertical portion of the canal is normal and filled with air.
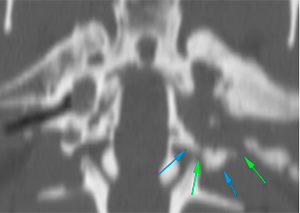
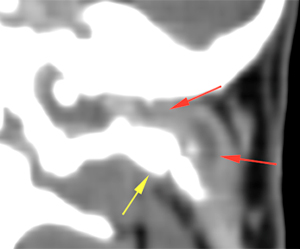
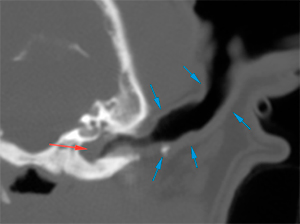
The petrous portion of the temporal bone is markedly sclerotic (green arrows), with irregular margins in the region adjacent to the inner ear (red arrows), which are not completely visible compared to the contralateral side (blue circle). No intracranial extension is observed.
After contrast administration, there is a marked and slightly heterogeneous enhancement of the left medial pterygoid muscle adjacent to the bulla (pink arrows).
The expansion of the tympanic bulla, previously described, causes a mild/moderate mass effect on the nasopharynx, which is slightly displaced towards the right with a mild focal narrowing of its lumen (orange arrows).
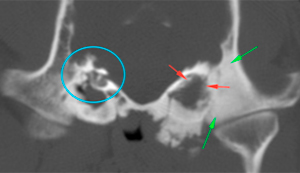
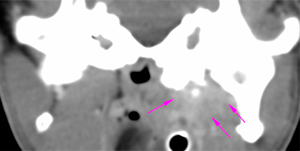
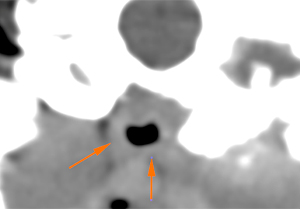
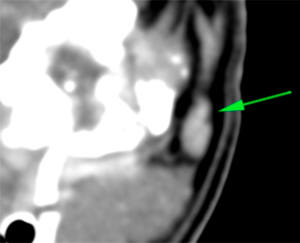
The right tympanic bulla has a normal morphology and wall (considering the patient’s breed) but shows a soft tissue attenuating material within it, that does not show postcontrast enhancement (red arrow). The wall of the right external ear canal is slightly thickened, with small mineralizations (blue arrows), although the lumen is filled with air.
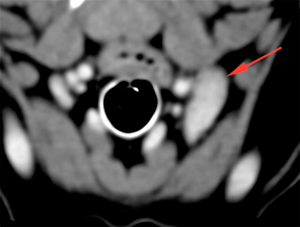
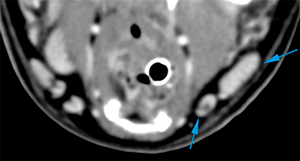
The parotid (green arrow), mandibular (blue arrows) and left medial retropharyngeal (red arrow) lymph nodes are asymmetric and enlarged (compared to the contralateral side), showing homogeneous post-contrast enhancement.
Diagnosis
- Left ear:
- Lesion in left tympanic bulla involving the horizontal portion of the external ear canal, consistent with severe chronic otitis media and externa. However, a concomitant process such as a cholesteatoma cannot be completely ruled out. Secondary to this lesion, there is:
- Osteomyelitis of the petrous portion of the temporal bone and sclerosis, with consequent otitis interna.
- Enhancement of the left medial pterygoid muscle and soft tissues adjacent to the bulla, consistent with extension of the infectious process/myositis.
- Mild mass effect causing mild focal nasopharyngeal stenosis.
- Right ear:
- Findings consistent with mild otitis externa and media, with preservation of the normal morphology of the tympanic bulla.
- Lymphadenopathy of the parotid, mandibular and left medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes: reactive most likely.
Comments
Otoscopy and sampling of the left middle/external ear is recommended in order to reach a definitive diagnosis.
The following article might be of interest:

No comment yet, add your voice below!